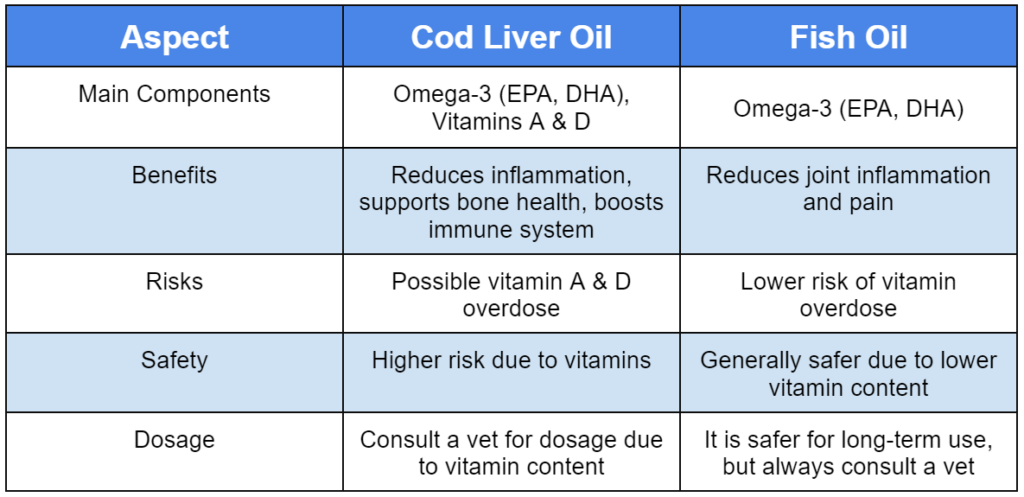
Fish oil is more effective for arthritic pains than cod liver oil; which is derived from cod and contains omega 3 fatty acids.
A common practice for pet owners who treat their dog’s arthritis is to prefer the most natural supplement that can reduce pain and improve flexibility of the pets most especially dogs. Out of all of these ideas, cod liver, and fish oil have proven to be the most effective since they have anti-inflammatory properties, and there might be other advantages for the individuals that are using them. Regardless, they possess a different nutritional label and that is certain to affect dogs’ overall well-being.
The kind that contains omega-3 fatty acids like cod liver oil and fish oil are also remarkable but they contain lower inflammatory indices. However, which of them is actually able to address a common issue for pet owners: the issues of joint pains in regards to their animals and the effects caused by the same such as restriction of movement? Let’s find out!
Basic differences between Cod liver oil and Fish oil
Cod liver oil has EPA and DHA omega-3 fatty acids and vitamins A and D. One way that inflammation and the pain of arthritis related with thermal hyperalgesia can be decreased is by Omega 3 fatty acids. Although there are numerous positive effects of taking vitamin D supplements for the immune response, bones, and other tissues, vitamin A is significant for bones only.
It is very dangerous to give a dog too much cod liver oil since it can lead to the fatal overdose on vitamins A and D.
Fish Oil For Dogs:
Cod liver oil contains vitamin A and D and omega-3 fatty acids that are gotten from fish oil though in lesser quantities. Polyunsaturated fats are tender good for bringing down the inflammation and joint mechanism ache often encountered with arthritis. It is crucial to note that cod liver oil and fish oil for many people are less safe regarding vitamin A and D toxicity.
2. Dilated Cardiomyopathy (DCM)
Lately, the U. S Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has stated it is looking into a possible correlation between consumption of products with grain-free’ diets and DCM in dogs. However, more on this is being researched and certain diets where grains are limited, especially the ones filled with legumes or potatoes can increase the risk of DCM.
3. Higher Fat Content
A few grain-free diets are rich in fat; thus, making your dog put on some weight or develop pancreatitis if they are prone.
4. Cost
Dietary plans are generally costly and grain-free diets are comparatively pricier than regular dog foods, and this can be a drawback for many people.